Diamond Drilling Tools & Applications
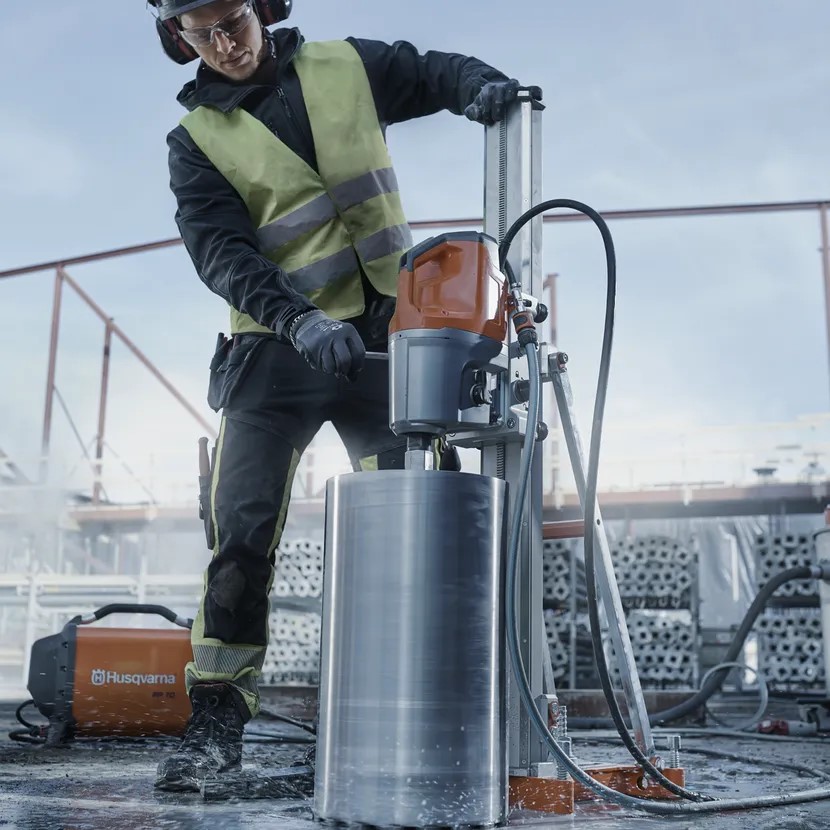
When construction crews need to cut through reinforced concrete or create precise cores, they turn to one of the most effective tools in the industry: diamond drilling equipment. These specialized tools have completely changed the way contractors approach challenging materials, offering precision and durability where traditional methods fall short.
Understanding how these tools work and their applications can help contractors, engineers, and facility managers choose the right equipment for their projects. With over 60 years of experience operating and repairing diamond drilling equipment, we at Detroit Diamond Drilling are here to share our expertise.
What Are Diamond Drilling Tools, and What Sets Them Apart?
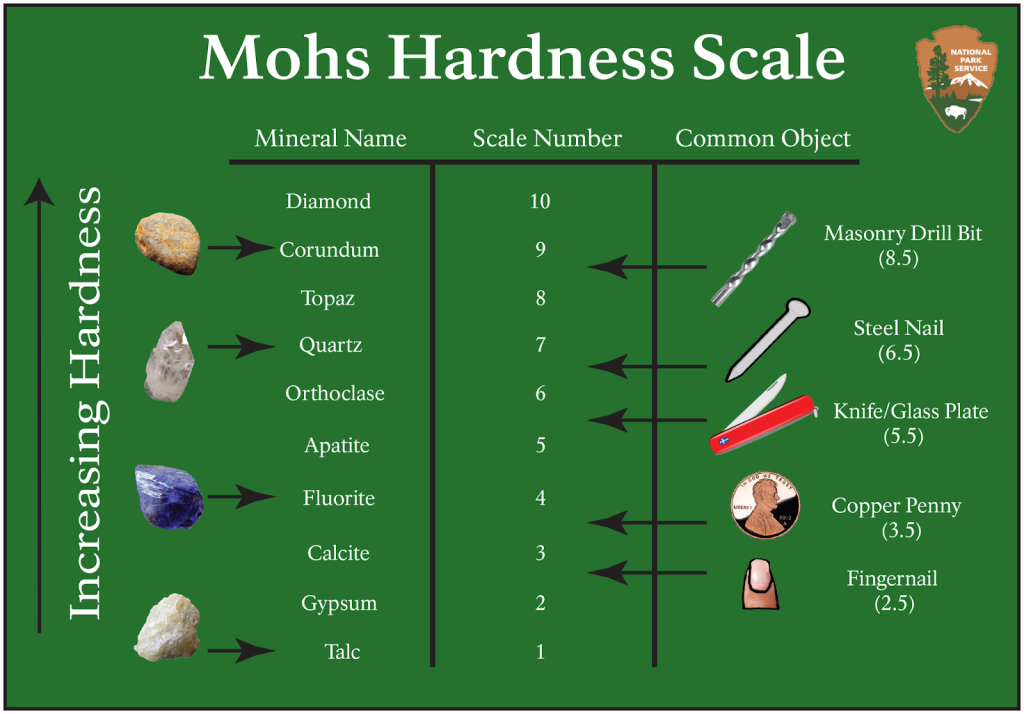
Diamond drilling tools use synthetic or natural industrial-grade diamonds fixed onto the cutting edge of drills. These diamonds, with a Mohs hardness of 10, cut through some of the hardest construction materials, including reinforced concrete, asphalt, and natural stone. While a standard drill might struggle or fail entirely against these materials, diamond drilling tools slice right through with accuracy and minimal structural damage.
Unlike percussive methods, which break material by impact, diamond drilling uses a spinning motion (rotary) to cut through material via abrasion. The tiny diamonds on the tool’s cutting edge grind material down through constant friction as the drill rotates, eliminating the structural vibrations and damage caused by hammering tools. In reinforced concrete, for instance, the diamonds wear away the material and cement while gradually slicing through embedded steel rebar, all while keeping complete precision.
Key Components of Diamond Drilling Equipment
Drill Rigs: Stability and control rely on the drill rig, which supports vertical or angled drilling in various settings.
Core Drill Units: These machines house the motor, rotary system, and drill head; they drive the rotation necessary for cutting.
Coolant Systems: Water-based coolants circulate through the bit to reduce heat, flush out debris, and minimize wear. As the bit cuts, water or synthetic coolant flows through the system, cooling the bit, lubricating the surface, and clearing the resulting groove of mud and grindings.
Rotary Mechanisms: The high-torque rotary produces a strong and continuous force, driving consistent cutting speed with the ability to adapt to different materials.
Wet vs. Dry Diamond Bits
Wet Bits are used with water to reduce dust and improve cooling, which is essential when drilling dense materials. The continuous water flow prevents overheating and extends the life of the drill bit during long projects in concrete and masonry.
Dry Bits operate without coolant and are an optimal choice for situations lacking access to water, especially on job sites with electrical hazards. These bits have enhanced diamond bonding to perform in higher temperatures without water cooling.
Segmented Diamond Bits
Designed for aggressive material removal, segmented bits have grooves between segments (gullets) that allow heat to release more effectively during use. These gaps also make for faster cutting and improved debris clearance.
Applications:
- “For general purpose drilling of granite and marble,” states Husqvarna.
- Rapid material removal in thick concrete sections
- Situations requiring fast cutting speeds over smooth finish quality
Turbo Diamond Bits
Turbo diamond bits use a serrated rim to deliver a perfect balance between cutting speed and smoothness. The turbo segments create a turbulent airflow that helps cool the bit and clear debris without affecting accuracy.
Applications:
- Medium-hard materials like marble or limestone
- Decorative stone cutting where moderate finish quality is required
- General-purpose concrete cutting in construction applications
Continuous-Rim Diamond Bits
These bits provide the smoothest cut possible by using a solid diamond layer around the edge. However, this bit does operate at slower speeds than other segmented bits.
Applications:
- Tile, glass, and brittle materials that require precision without chipping
- Finish work where it is essential to maintain edge quality
- Thin materials that require delicate handling
Standard Core Drills
These cylindrical drills pull core samples for material testing, structural assessments, and anchoring. At the heart of the system is the diamond-embedded drill bit—a steel cylinder with diamond segments on its cutting edge. This technology allows for the retrieval of cylindrical samples, or “cores,” which are necessary for discovering what lies beneath the surface.
Applications:
- Sampling of concrete in old bridges or dams to check the condition of the structure
- Creating access holes for HVAC, electrical wiring, or plumbing installations
- Custom hole placements inside hospitals, cleanrooms, or data centers
Extended-Length Core Drills
Designed for deep-core extraction, extended-length drills can handle depths beyond 1 meter, making them popular in geological and mining applications. These specialized tools maintain cutting precision even at significant depths while preserving the exact structure of soil or rock formations.
Applications:
- Soil and foundation engineering to test ground stability, load-bearing strength, and water content
- Mining surveys for detailed core records to locate valuable mineral deposits
- Deep foundation testing in commercial and infrastructure projects
Handheld Core Drills
Handheld Drills boast portability and are usually used for shallow holes and small diameters. These units offer flexibility for quick jobs and tight access, but their depth and diameter abilities are limited.
Applications:
- “Suitable for light applications such as ventilation, plumbing pipes, electrical sockets and cables,” according to Husqvarna.
- Drilling in confined spaces where larger equipment can’t fit
- Taking shallow samples for structural assessments in accessible areas
Industry-Specific Applications
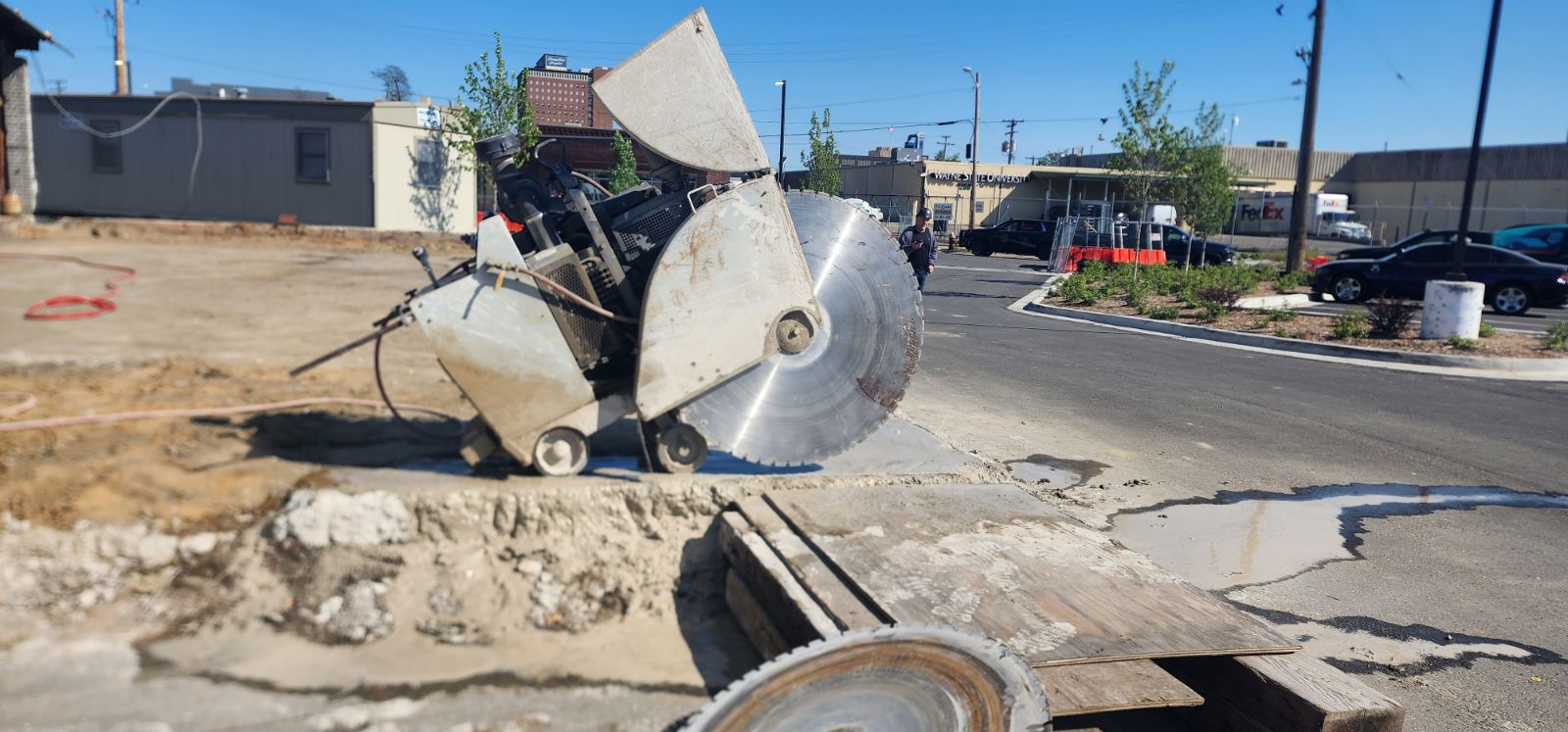
Construction and Infrastructure: Diamond drilling cuts clean openings for doors, creates expansion joints, and cuts trenches in concrete floors. Contractors get smoother, cleaner cuts that require less finishing work compared to jackhammers and other traditional methods.
Roadway and Asphalt Work: Road crews use diamond drilling to cut through concrete highways, collect samples to test road quality, and make precise cuts in bridge surfaces. The clean cutting action keeps edges intact when digging trenches for cables or pipes, and maintains road surface quality when installing sensors under asphalt.
Municipal and Industrial: City crews drill into concrete sewer tunnels and storm drains using these tools. For underwater work, diamond drilling equipment stays stable and cuts accurately even when submerged, making it ideal for marine construction and dam work.
Leading Manufacturers of Diamond Drilling Equipment
Don’t have the tools you need for the job? Here are some of some of the best brands for diamond drilling products:
Hilti: Known for reliable handheld core drills and diamond bits, particularly popular for anchor installations and utility penetrations in construction.
Husqvarna: Leading manufacturer of both handheld and rig-mounted drilling systems, recognized for innovative cooling systems and durable diamond bits.
Milwaukee: Well-regarded for portable drilling systems with contractor-friendly features like ergonomic designs and powerful motors for handheld applications.
The Takeaway
Successful use of diamond drilling equipment is just as much about selecting the right tool as it is about experience. When used for the proper applications, diamond drilling tools have the potential to save contractors, engineers, and facility managers time and money when tackling even the toughest projects.